- Home
- Fundamentals of Email Marketing
- AI in E-Commerce: Practical Us ...
The term “artificial intelligence” was mentioned for the first time in the 1950s, and for over half a century it was more of a buzzword than an actual tool. Nonetheless, in the last three to four years, AI went to a full-blown acceleration due to the emergence of large language models and generative AI systems that suddenly made AI far more capable, accessible, and scalable.
Now we have a chance to witness this transformation unfold across many industries. But e-commerce is where the growth of AI has become truly exponential. The reason is simple: digital commerce generates more data, more decisions, and more customer touchpoints than almost any other sector. And AI thrives in exactly that kind of environment.
In this article, we’re going to explore how to use AI in e-commerce—what makes it so powerful, what kinds of challenges it solves, and what real-world examples can teach us about applying it strategically.
Why AI Is a Must-Have for E-Commerce in 2025
At some point, AI in e-commerce stopped being a nice-to-have and became the foundation beneath how online retail functions. This transition was happening so smoothly that no one now can probably say when it stopped being some far-off sci-fi future and turned into the workflows we’re building, the products we’re recommending, and the customer questions we’re (not) answering.
Regardless of the timeline, today we have more data than anyone can realistically handle. The same goes for more customer touchpoints and substantially less room for error. The workload and pressure from it grew tremendously in the last years, making many employees feel overwhelmed. According to a recent survey from PwC, 45% of employees had to learn new skills and technologies to be able to cope with their job tasks.
The fact that AI is stepping in in many areas, e-commerce included, and taking over some of the tasks is only logical. In the end, it can respond faster than we ever could and scale things that used to depend on headcount.
We already see AI in e-commerce examples all around us—intelligent search bars that actually understand what we type, product recommendations that feel eerily spot-on, email flows that somehow land at the perfect moment. But that’s surface-level. It will be fair to say that AI and e-commerce are no longer separate concepts but that they are merging into a unified system.
What’s even more significant is how AI in e-commerce has transformed customer experience. We’ve moved far beyond basic personalization—what we see now is hyper-personalization, driven by real-time behavior, context, and intent. AI doesn’t just suggest similar products; it understands when someone’s likely to buy, what messaging they’ll respond to, and how to guide them without friction.
On the back end, the impact is just as deep. Smarter inventory, dynamic pricing, faster support—AI for e-commerce reduces friction everywhere. For businesses, that means better efficiency. For customers, it means everything just works. And since the integration of AI in e-commerce has gone so far, ignoring it is not an option anymore.
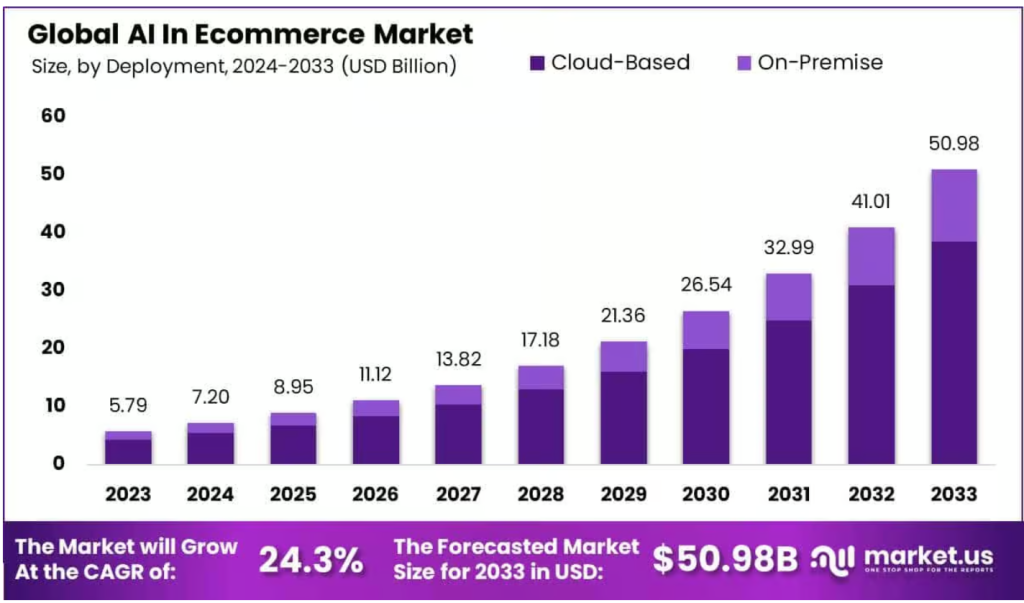
Real AI E-Commerce Use Cases & Implementation Tips
Now that AI in e-commerce has moved from theory to real infrastructure, the next question is what it actually looks like in practice. Where does it show up? How do you start using it? And more importantly—how do you use it well?
Below are some of the most impactful areas where artificial intelligence in e-commerce is already driving real results, supported by actual tools and examples.
A. Customer experience enhancements
Personalized recommendations
This is the most familiar face of AI in online shopping—and one of the most effective, too. Algorithms analyze browsing, purchase history, and real-time behavior to suggest products a customer is likely to want before they even think of searching for them.
Tool in action: Amazon’s recommendation engine accounts for up to 35% of total revenue, showing just how embedded and powerful this feature can be.
Smart search & visual discovery
Gone are the days when a misspelled word meant zero results. Now AI for e-commerce search understands synonyms, intent, and even typos. Visual discovery goes further—allowing users to upload an image and instantly find similar items.
Tool in action: ASOS’s visual search tool and Google Cloud retail search use AI to interpret intent and images, returning more relevant results and increasing session time.
AI chatbots & conversational interfaces
A while ago chatbots used to be rather useless and frustrating. Now, thanks to natural language processing, they’ve become actually helpful. AI e-commerce chatbots don’t just answer FAQs—they guide users through checkout, handle returns, and make personalized suggestions in the process of a conversation
Tool in action: For example, Sephora’s chatbot on Messenger can provide you with makeup tips and even suggest makeup brands based on an uploaded photo of a celebrity.
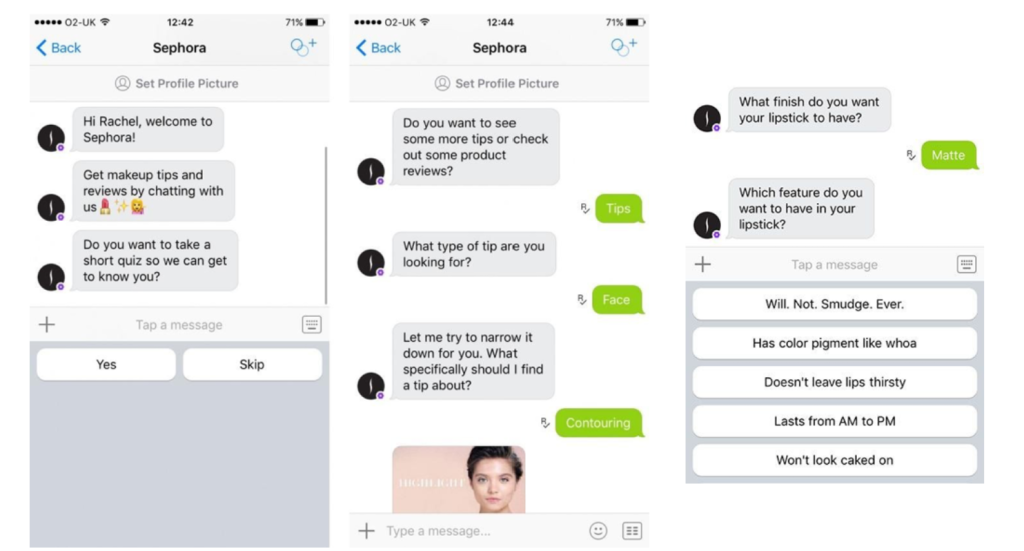
B. Content & copy automation
Generative content creation
Using AI in e-commerce also means writing less—and better. AI tools can now generate product descriptions, promotional headlines, and even entire email flows based on brand voice and past campaign data.
Tool in action: Such tools as Jasper AI and Copy.ai are widely used to create thousands of product descriptions at scale, freeing up teams for more strategic work.
C. Operations & supply chain
Forecasting, inventory & pricing
This is the area where AI in e-commerce has a truly massive impact. By analyzing historical trends, seasonality, and live demand, AI helps brands restock before items run out and price dynamically based on market shifts.
Tool in action: Zara uses AI to analyze sales data in real time, adjusting inventory and pricing across stores. This massive AI usage resulted in significant operational gains for the company, reinforcing its rapid-response model.
AI-driven product design & pre-sales
Some companies don’t even wait to make a product—they let AI test its market potential first. Alibaba’s “see now, buy now” approach lets them generate product mockups and test engagement before investing in production.
Tool in action: Using AI-generated visuals, Alibaba’s platform increased click-through rates by 13% and boosted conversions.
Application of generative AI tools across a wide range of situations on Alibaba

D. Ethics, trust & customer sentiment
AI-powered sentiment analysis
When you have thousands of reviews and support tickets to deal with daily, AI helps to make sense of it all. It can identify pain points, surface emerging issues, and even spot language trends.
Tool in action: Tools like MonkeyLearn and Lexalytics turn unstructured customer feedback into structured insights—without having to manually go through every comment.
Ethical AI practices
The more powerful AI and e-commerce become together, the more critical it is to use them in a responsible way. Brands must make sure that their systems are fair and transparent and consider privacy concerns.
Implementation tip: Build cross-functional AI review teams, include customer feedback loops, and always align your tools with evolving data privacy regulations.
Success in Action: AI in E-Commerce Examples
While some companies are just starting to experiment with AI, others have already embedded it deep into their workflows and are seeing measurable impact. Let’s look at some real-life AI examples from some of the most established, successful brands out there for some AI inspiration.
✨ eBay
With over 2.3 billion active listings, eBay faces the kind of scale that makes manual processes impossible. Adoption of generative AI by the company helps sellers auto-fill product titles, descriptions, and item specifics based on just a photo or a few keywords, which makes the listing process for many considerably smoother. The rollout has touched over 10 million sellers already, improving the efficiency of listings and consistency while drastically reducing the time it takes to get products live.
✨ Swarovski & Caleres
Since about 70% of online shoppers abandon their carts, companies have been looking for ways to prevent this unpleasant phenomenon ever since. Since reasons for cart abandonment are often related to distraction or not being able to find the exact right product, both Swarovski and Caleres implemented AI-powered solutions that now guide users to more relevant products based on behavior, context, and browsing intent. As a result, Swarovski managed to achieve a 10% boost in sales directly attributed to AI. Similarly, Caleres significantly elevated the personalized shopping experience with machine learning-powered product recommendations, driving a notable year-over-year increase in revenue from recommended products.
✨ Amazon (Rufus)
Amazon’s newest AI shopping assistant, Rufus, is a sign of what’s coming next. It’s designed to interact like a personal guide—helping users compare products, refine searches, and get recommendations without bouncing between pages. Behind the scenes, Amazon is also developing autonomous agents to automate and optimize retail workflows, from inventory movement to pricing strategies—something that can redefine the backend of online shopping entirely.
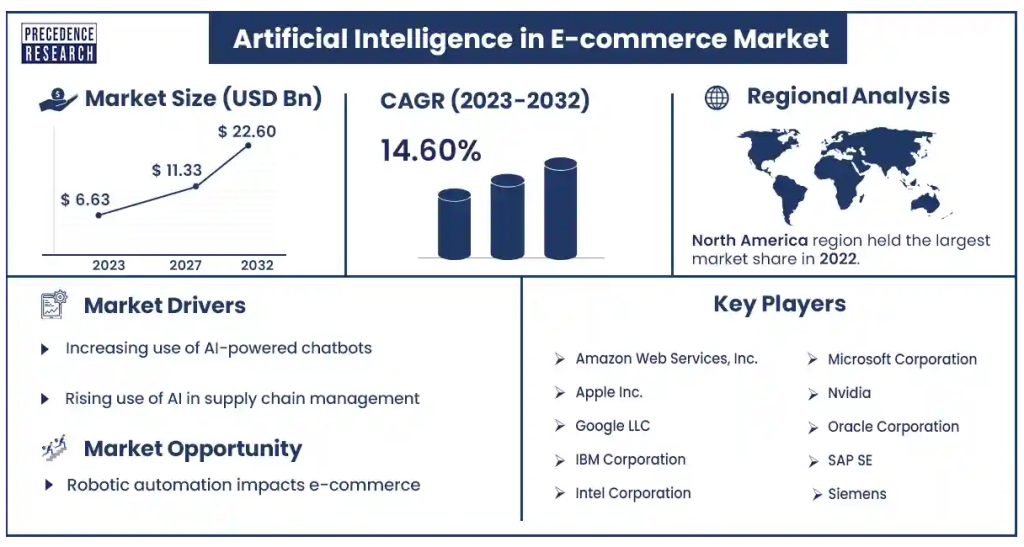
To Sum Up
AI has moved from theoretical to practical, from novelty to necessity. It’s no longer a question of if it belongs in e-commerce, but how it’s going to shape the way businesses operate.
The good news is, using AI in e-commerce doesn’t have to be a massive, all-at-once transformation. Each company can find its own entry point—whether it’s smarter search, better recommendations, or more accurate forecasting. What matters is seeing it not as a quick fix, but as a long-term strategy for building a smarter, more adaptive system.
Because as AI becomes more naturally integrated into everyday life, the gap between companies who experiment with it—and those who don’t—will only grow. And with each passing year, that gap gets harder to close.

